Enhanced Breathing Protection than N95 Grade Paper Masks
Problems with disposable masks
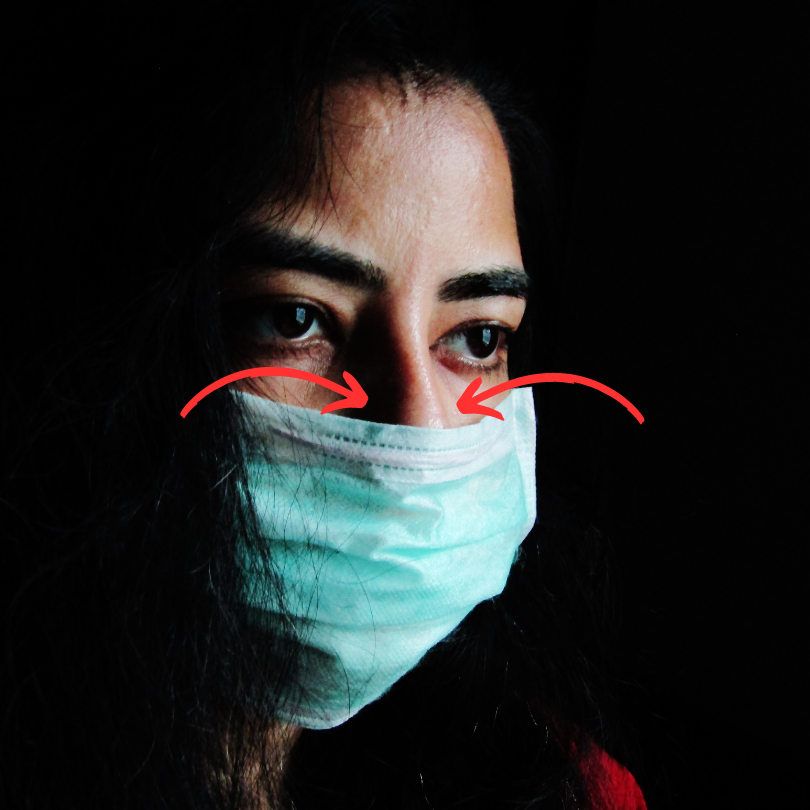
- The sealing is not tight. Even if the sealing seems to be OK, it is not reliable enough in actual application.
 |
 |
- Disposable N95 masks are limited by the actual flow area of the face, and the filter material filtration grade cannot be too high; otherwise it will increase breathing resistance and affect normal use.
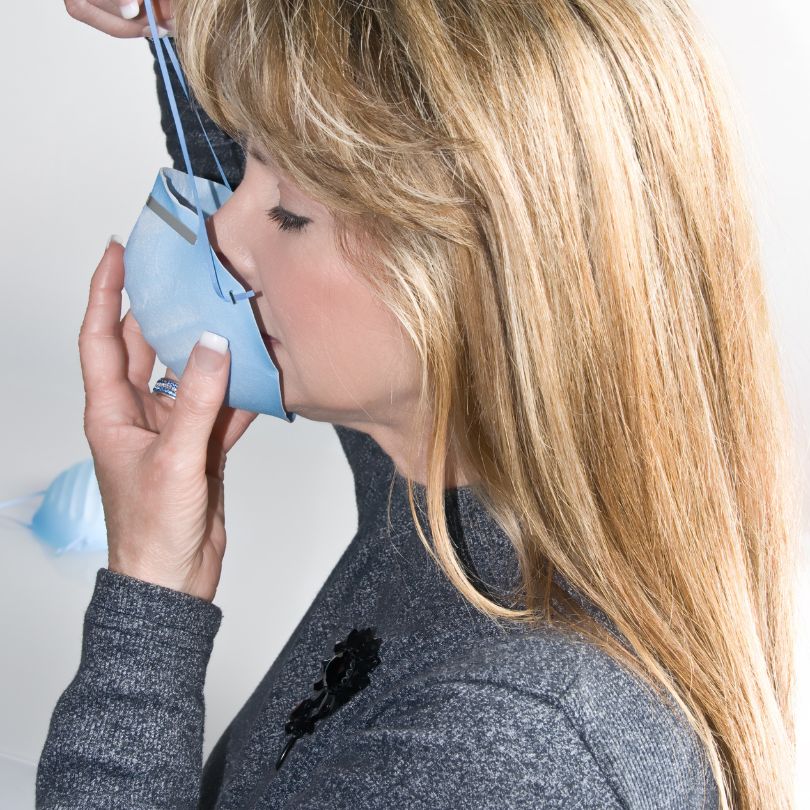
- Moisture in exhaled breath reduces filtration efficiency and increases respiratory resistance.
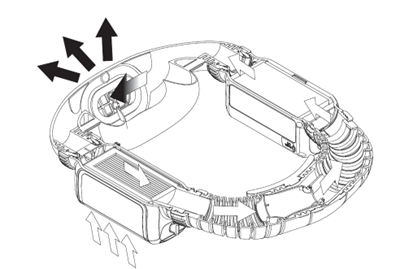
How does AYO HC achieve a superior sealing fit?
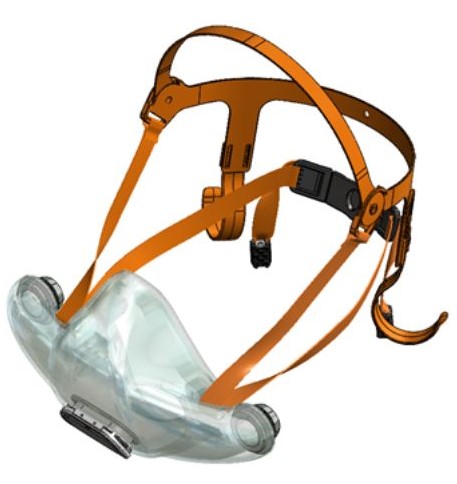
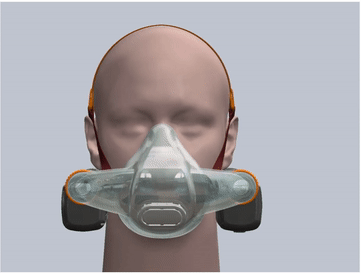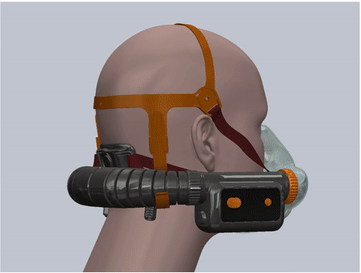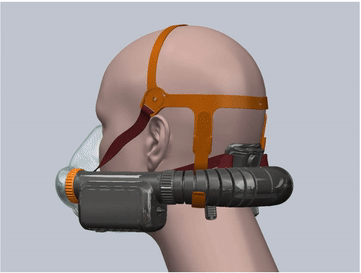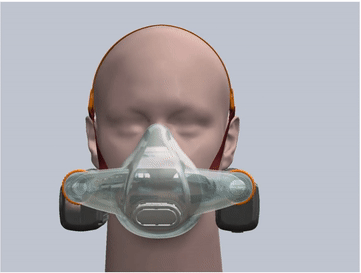
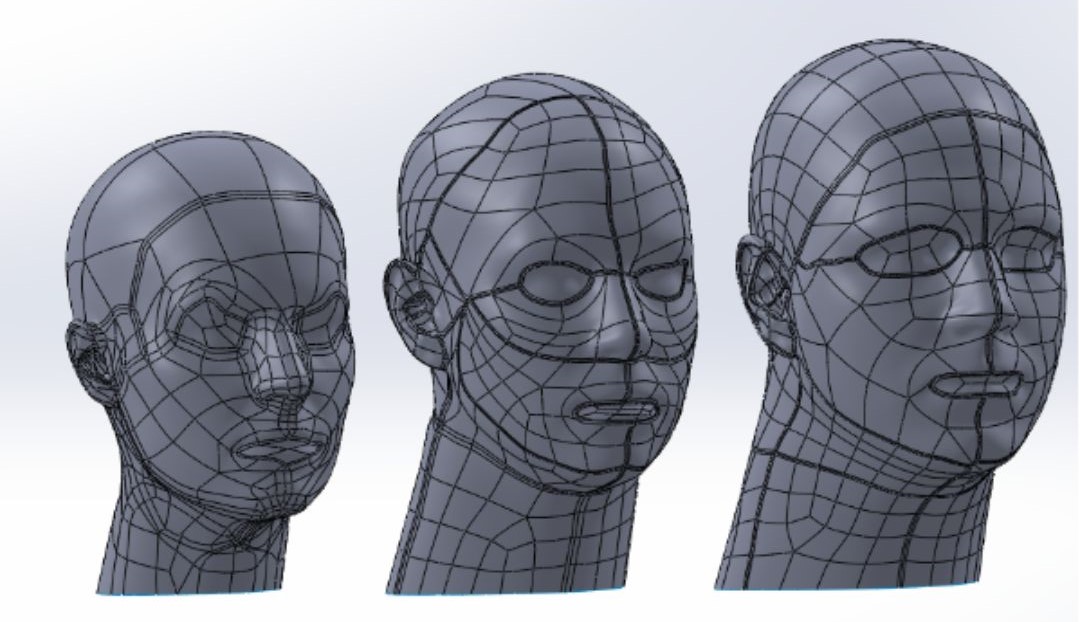
- The mask is made of soft silicone material and is specially designed for 3 head sizes in 3 mask sizes: large, medium and small, which can fit 99.7% of human face contours. This greatly improves the sealing and tightness compared to disposable masks.
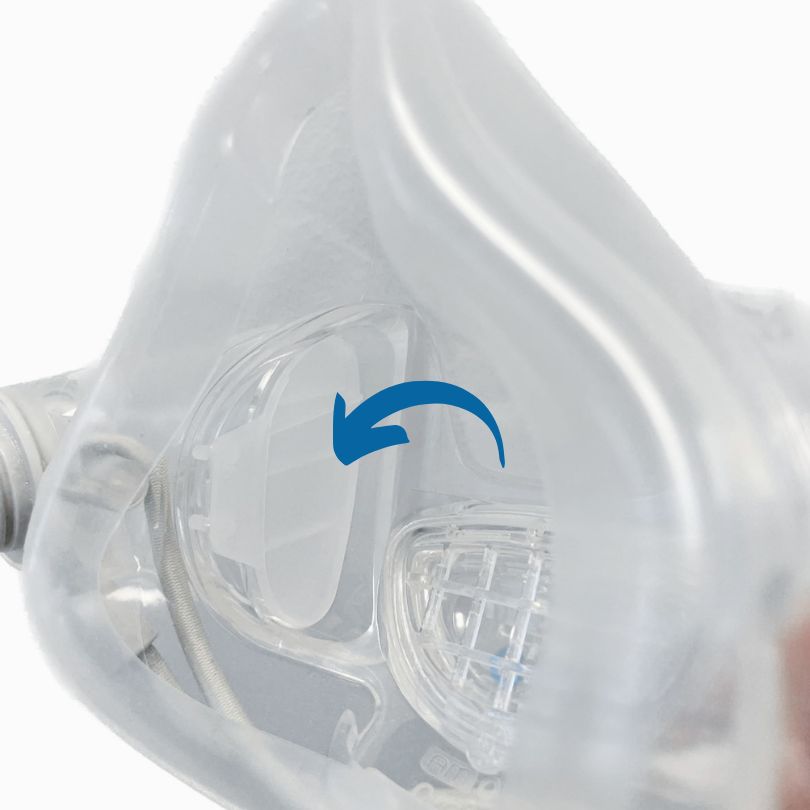
- The design of the mask cushion is also unique, with a sufficient elastic range, and is made very thin, which further enhances the sealing fit between the mask and the face.
- The overall fit factor exceeds 2000, which is 20 times higher than the N95 level.
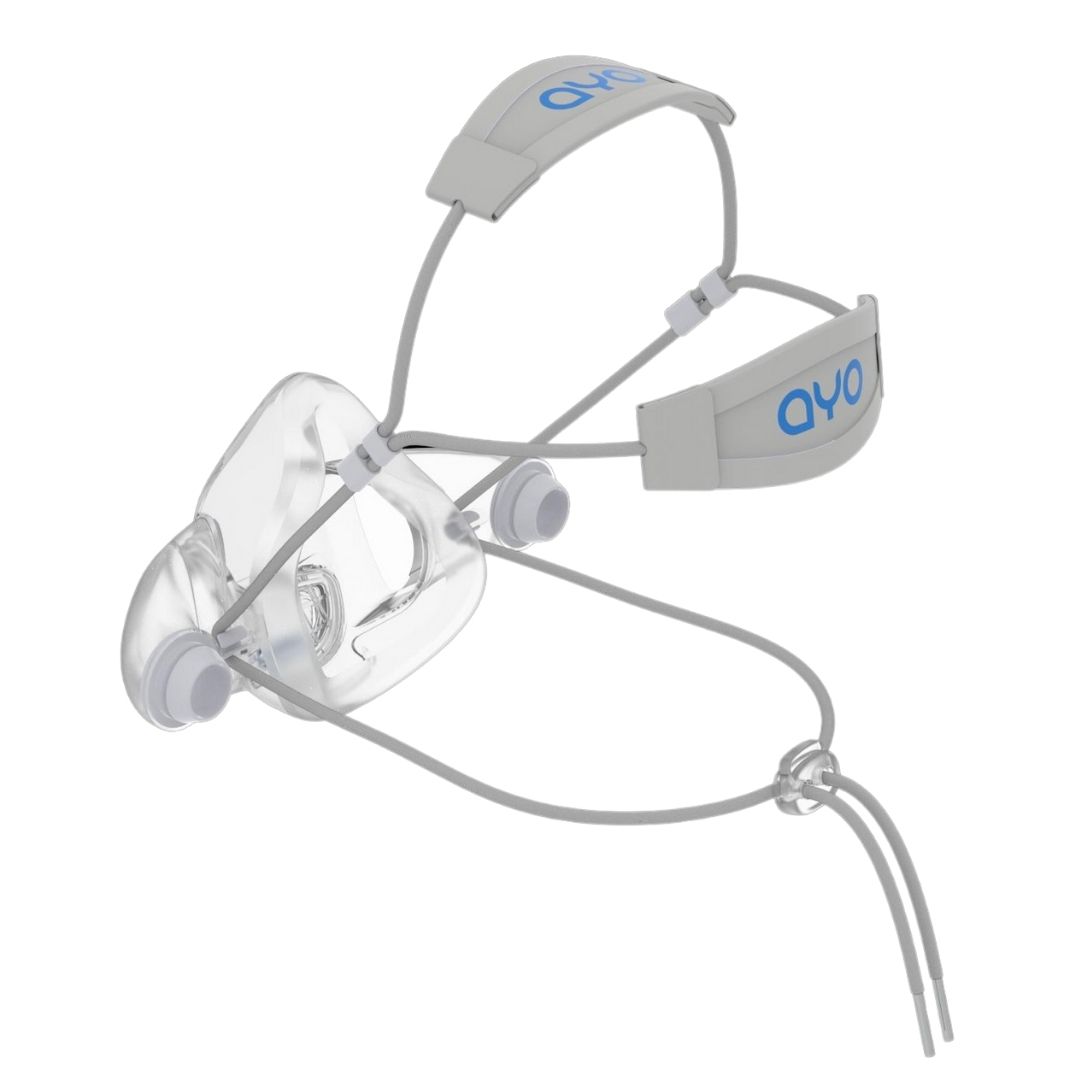

silicone mask
Designed for three head sizes, suitable for 99.97% of human face contours
How does AYO HC achieve higher filtration efficiency?
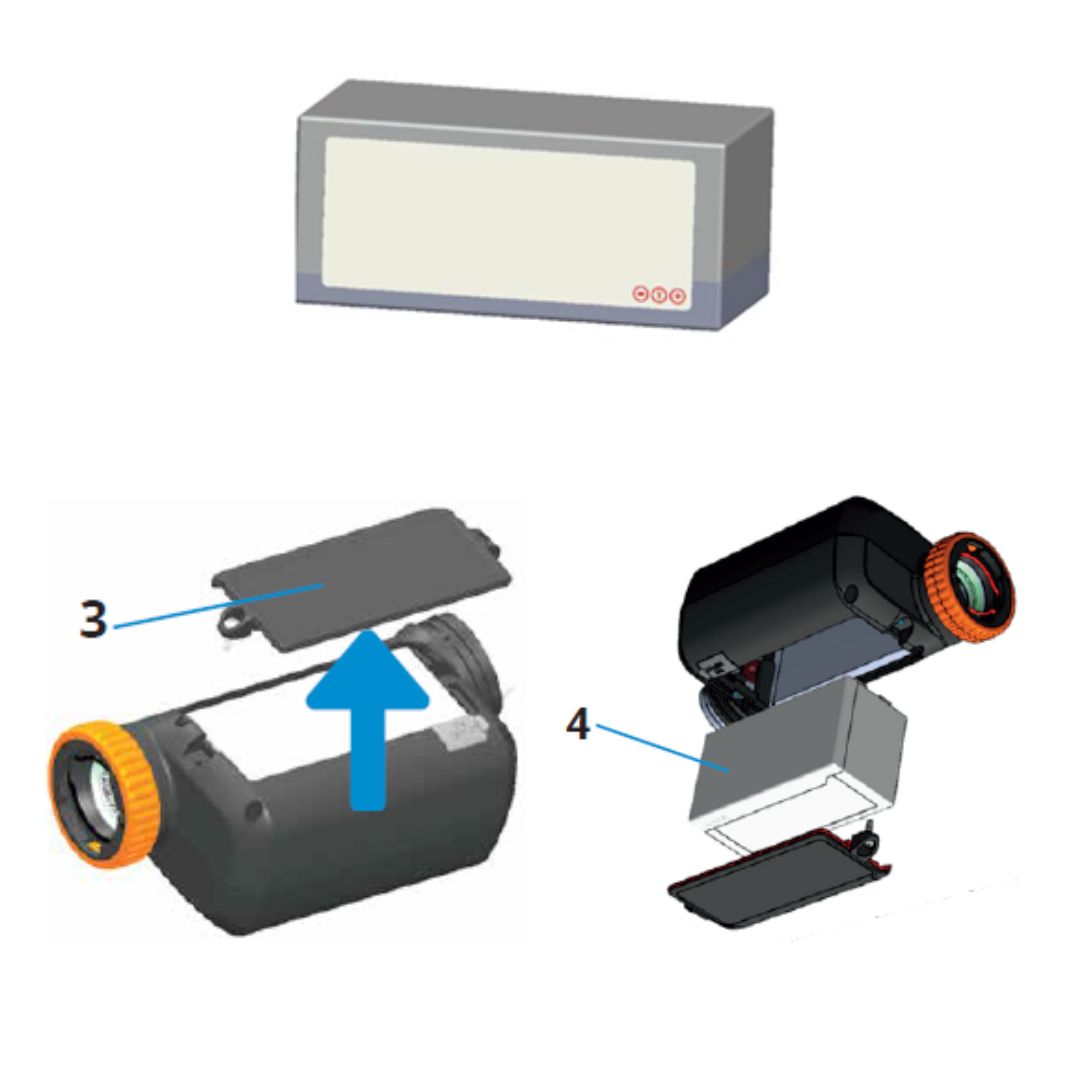
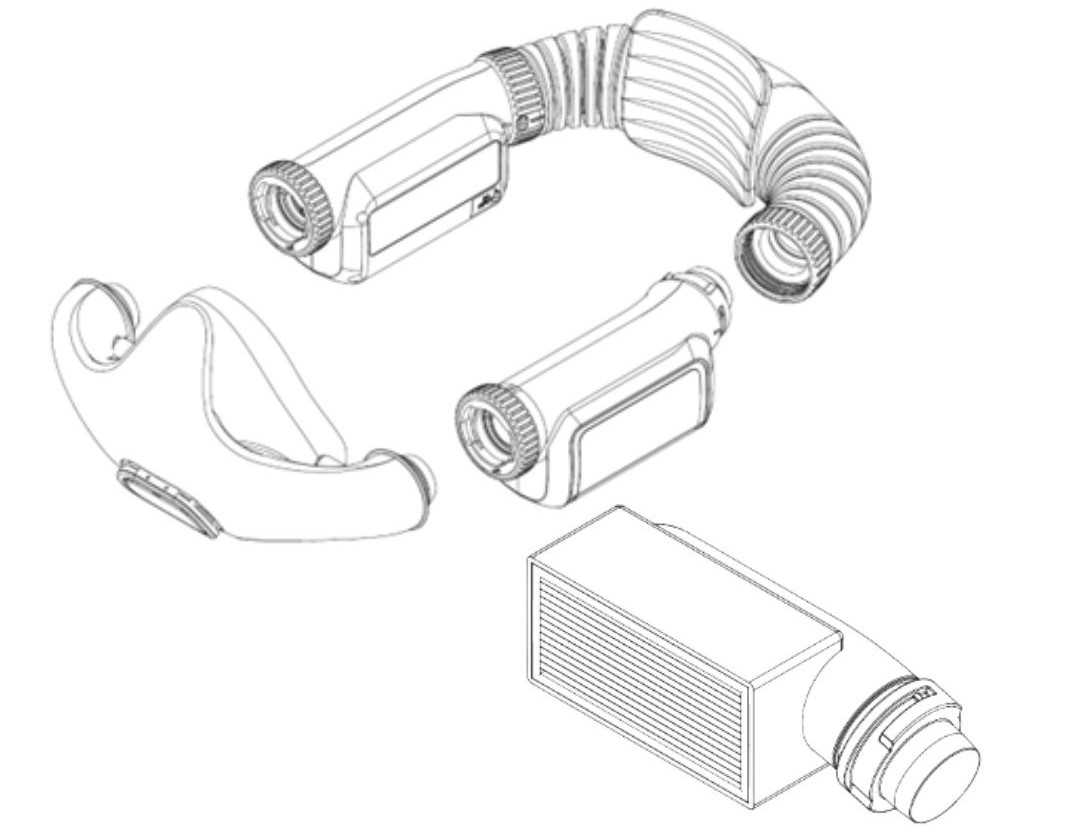
- Using a higher level of filter material than N95 as the main filter element, the filtration efficiency for particles 0.3um and above is >99.9%, compared to the N95 standard of 94%, achieving a protective effect 50 times higher than the N95 level.
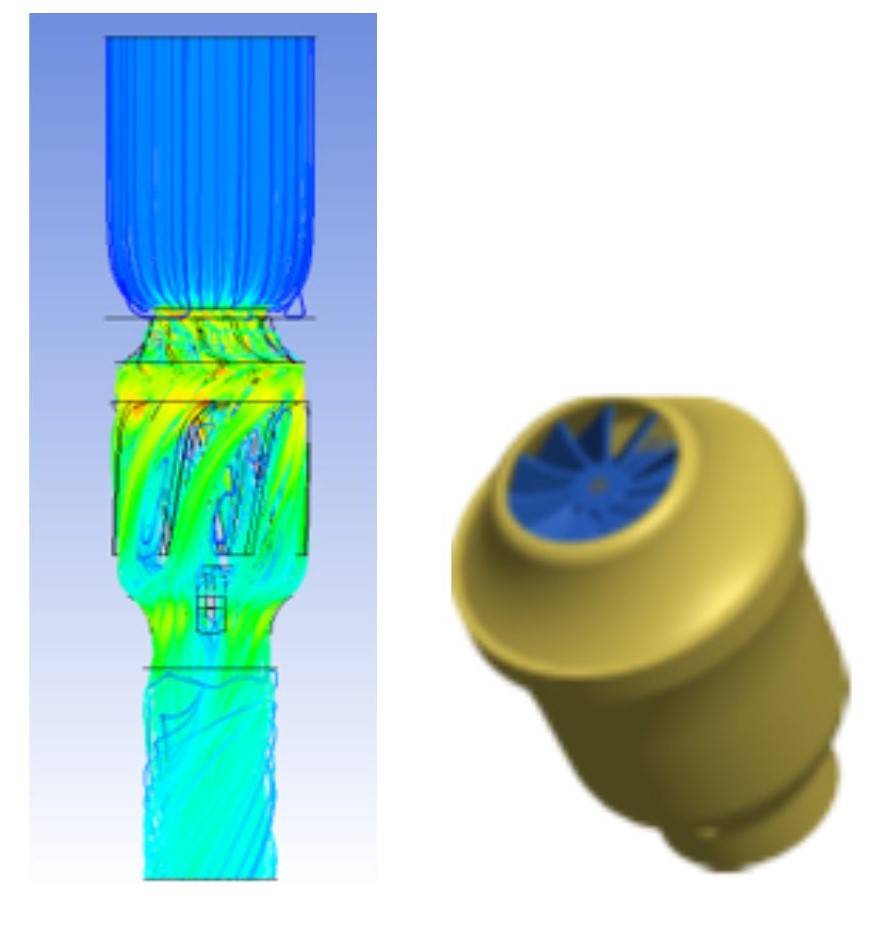
- At the same time, the filter element adopts pleated filter material, which greatly increases the actual effective flow area. Although the filter material level is improved, the airflow resistance can still be controlled within an acceptable range, and the peripheral size of the filter element can still be kept small.
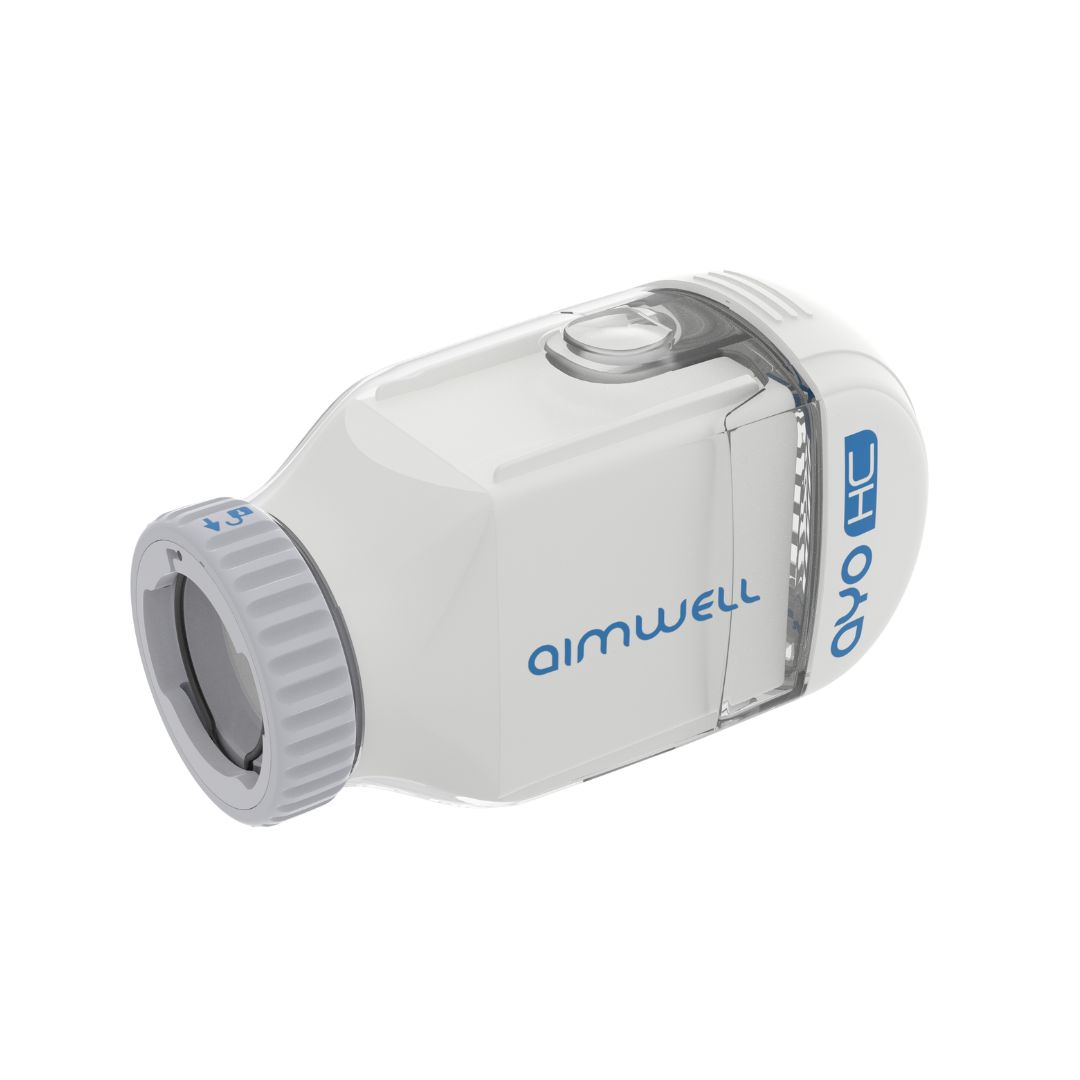

air intake module

How does AYO HC prevent moisture from reducing filtration efficiency?
The built-in air inlet valve of the silicone mask prevents moisture in each exhalation from entering the main filter element, thereby preventing the reduction of filtration efficiency and increasing in breathing resistance caused by moisture, thus extending the life of the filter.